
Arthroscopy is a procedure that orthopaedic surgeons use to fantasize and treat problems inside a joint.
The word arthroscopy comes from two Greek words,” arthro”( joint) and” skopein”( to look). The term literally means” to look within the joint.” During elbow arthroscopy, your surgeon inserts a small camera, called an arthroscope, into your elbow joint. The camera displays filmland on a TV screen, and your surgeon uses these images to guide atomic surgical instruments.
Because the arthroscope and surgical instruments are thin, your surgeon can use veritably small lacerations( cuts), rather than the larger gash demanded for open surgery. This results in lower pain for cases, lower common stiffness, and frequently shortens the time it takes to recover and return to favorite conditioning.
Elbow arthroscopy has been performed since the 1980s. It has made opinion, treatment, and recovery from surgery easier and faster than was formerly allowed
possible. Advancements to elbow arthroscopy do every time as new instruments and ways are developed
Elbow deconstruction
The elbow is a complex common formed by the joining of three bones
- The humerus( upper arm bone)
- The ulna( forearm bone on the pinky cutlet side)
- The compass( forearm bone on the thumb side)
The shells of the bones where they meet to form the elbow joint are covered with articular cartilage, a smooth substance that protects the bones and acts as a natural bumper to absorb forces across the joint. A thin, smooth towel called synovial membrane covers all remaining shells inside the elbow joint. In a healthy elbow, this membrane makes a small quantum of fluid that lubricates the cartilage and eliminates nearly any disunion as you bend and rotate your arm.
On the inner and external sides of the elbow, ligaments( collateral ligaments) hold the elbow joint together and help disturbance.
The elbow joint is girdled by muscles on the front and back sides. In addition, the three major jitters that cross the elbow joint are located near to the common shells and capsule and must be defended during arthroscopic surgery.
The elbow joint allows two introductory movements bending and uncurling( flexion and extension) and forearm gyration( pronation — win down, and supination — win up).
Normal bending and uncurling movements do at the joining of the humerus and ulna bones. Forearm gyration occurs at the joining of the ulna and compass and is also told by muscles and ligaments further down the forearm and at the wrist joint.
When Is Elbow Arthroscopy Recommended?
Your croaker
may recommend elbow arthroscopy if you have a painful condition that doesn’t respond to nonsurgical treatment. Nonsurgical treatment includes rest, physical remedy, and specifics or injections that can reduce inflammation. Inflammation is one of your body’s normal responses to injury or complaint. In an injured or diseased elbow joint, inflammation causes swelling, pain, and stiffness.
Injury, overuse, and age- related wear and tear and gash are responsible for utmost elbow problems. Elbow arthroscopy may relieve painful symptoms of numerous problems that damage the cartilage shells and other soft apkins girding the joint. Elbow arthroscopy may also be recommended to remove loose pieces of bone and cartilage, or release scar towel that’s blocking stir.
Common arthroscopic procedures include
- Treatment of tennis elbow( side epicondylitis)
- junking of loose bodies( loose cartilage and bone fractions)
- Release of scar towel to ameliorate range of stir
- Treatment of osteoarthritis( wear and tear and gash arthritis)
- Treatment of rheumatoid arthritis( seditious arthritis)
Treatment of osteochondritis dissecans( exertion affiliated damage to the capitellum portion of the humerus seen in flier or turners)

Treatment of fractures
x-ray of elbow osteoarthritis
There are several elbow surgical treatments that are presently most effective when done as an open, traditional procedure. These include surgeries to
- Treat golfer’s elbow( medium epicondylitis)
- form the collateral ligaments
- Fix some types of fractures
- Perform elbow common relief( arthroplasty)
- relax the ulnar whim-whams( funny bone whim-whams)
Some advanced surgeries combine arthroscopic and open procedures in the same setting. For illustration, in a severe case of osteochondritis dissecans, a loose piece of bone may be removed arthroscopically, and the damaged area of the humerus may be treated with a bone graft using an open surgical fashion.
Planning For Surgery
Evaluations and Tests
Your orthopaedic surgeon may ask you to see your primary croaker
to make sure that you don’t have any medical problems that need to be addressed before your surgery. Blood tests, an electrocardiogram, or casketx-ray may be demanded to safely perform your surgery.
still, a more expansive evaluation may be necessary before your surgery, If you have certain health pitfalls. Be sure to inform your orthopaedic surgeon of any specifics or supplements that you take. You may need to stop taking some of these previous to surgery.
still, your arthroscopy will most probably be performed as an inpatient, If you’re generally healthy. This means you won’t need to stay overnight at the sanitarium.
Admissions Instructions
The sanitarium or surgery center will communicate you ahead of time to give specific details about your procedure. Make sure to follow the instructions on when to arrive and especially on when to stop eating or drinking previous to your surgery.
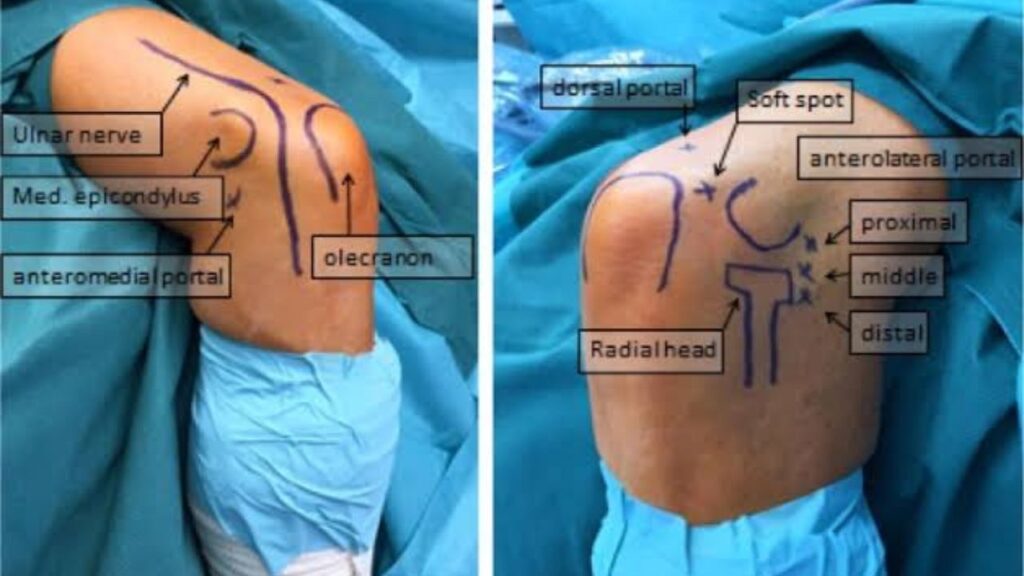
Anesthesia
Before the operation, a member of the anesthesia staff will talk with you about anesthesia options. Elbow arthroscopy is generally performed using general anesthesia, meaning you’re put to sleep.
Regional whim-whams block injections that numb just your elbow area are infrequently used in elbow arthroscopy because the deadening effect can last for a many hours after the procedure is completed. Although the deadening effect can help with managing pain, it prevents your surgeon from completing a careful whim-whams examination in the recovery room to make sure that the jitters that travel down your arm are performing well.
still, a indigenous anesthetic may be handed in the recovery room after your surgeon completes the whim-whams examination, If necessary for pain control.
content by best healthcare marketing agency.

